Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that affects the thin layer of tissue that covers the majority of your internal organs. This layer of tissue is known as the mesothelium, and it is found in several areas of the body, including the lungs, abdomen, heart, and testicles.
The majority of mesothelioma cases are caused by exposure to asbestos, a mineral that was commonly used in construction and manufacturing during the 20th century. Asbestos was used in a wide variety of products, including insulation, roofing materials, flooring, and automotive parts. When asbestos fibers are inhaled, they can become lodged in the lining of the lungs and other organs, causing inflammation and eventually leading to the development of cancer.
In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of mesothelioma in detail, as well as provide information on how to prevent exposure to asbestos.
Causes of Mesothelioma
As mentioned earlier, the primary cause of mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos. However, it is important to note that not everyone who is exposed to asbestos will develop mesothelioma. In fact, the risk of developing mesothelioma is relatively low, even among individuals who have been exposed to asbestos.
Other factors that may increase the risk of developing mesothelioma include:
- Age: Mesothelioma is more common in older individuals, with the majority of cases occurring in people over the age of 65.
- Gender: Mesothelioma is more common in men than women.
- Genetics: Some studies have suggested that certain genetic mutations may increase the risk of developing mesothelioma.
- Radiation exposure: Exposure to high levels of radiation has been linked to an increased risk of developing mesothelioma.
- Chemical exposure: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as vinyl chloride, may increase the risk of developing mesothelioma.
Symptoms of Mesothelioma
The symptoms of mesothelioma can vary depending on the location of the cancer and the stage at which it is diagnosed. However, some common symptoms include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Persistent cough
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Bowel obstruction
- Anemia
Diagnosis of Mesothelioma
Diagnosing mesothelioma can be challenging, as the symptoms of the disease are often similar to those of other conditions, such as lung cancer and pneumonia. Additionally, mesothelioma is a rare disease, and many healthcare professionals may not have experience diagnosing or treating it.
If mesothelioma is suspected, your healthcare provider will likely perform a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis, including:
- Imaging tests: These may include X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans to look for abnormalities in the affected area.
- Biopsy: A sample of tissue will be taken from the affected area and examined under a microscope to determine if cancer cells are present.
- Blood tests: These may be used to look for certain markers that are associated with mesothelioma.
Treatment of Mesothelioma
The treatment options for mesothelioma depend on several factors, including the location and stage of the cancer, as well as the overall health of the patient. Some common treatments include:
- Surgery: Depending on the location of the cancer, surgery may be used to remove as much of the cancer as possible.
- Chemotherapy: This involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: This involves the use of high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: This involves the use of drugs that help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
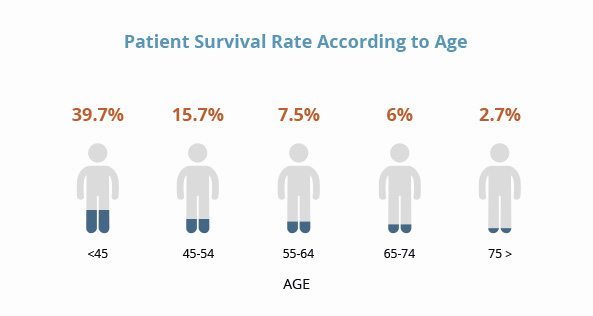
Mesothelioma Survival Rates by Stage
Mesothelioma survival rates vary based on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s age and overall health, and the type of treatment they receive. The most common staging system for mesothelioma is the TNM system, which categorizes tumors based on their size, extent of spread to nearby lymph nodes, and metastasis to distant organs. Here is a breakdown of mesothelioma survival rates by stage:
- Stage 1: In this stage, the cancer is localized to the lining of one organ and has not spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body. The 5-year survival rate for stage 1 mesothelioma is around 40% to 50%.
- Stage 2: In stage 2, the cancer has begun to spread beyond the original site and may have affected nearby lymph nodes. The 5-year survival rate for stage 2 mesothelioma is around 20% to 30%.
- Stage 3: At this stage, the cancer has spread extensively throughout the lining of one organ and may have invaded nearby organs or lymph nodes. The 5-year survival rate for stage 3 mesothelioma is around 10% to 20%.
- Stage 4: In the final stage, the cancer has spread to multiple organs or throughout the body, making it difficult to treat. The 5-year survival rate for stage 4 mesothelioma is less than 5%.
It’s important to note that these survival rates are based on statistical averages and may not accurately reflect an individual’s prognosis. Many factors can influence a patient’s survival, including their overall health, response to treatment, and access to quality care.
Factors That Affect Mesothelioma Survival Rates
As mentioned, several factors can influence a patient’s mesothelioma survival rate. Here are some of the most significant factors to consider:
- Age: Older patients tend to have lower survival rates than younger patients, as their bodies may not be able to tolerate aggressive treatments as well.
- Gender: Women tend to have higher survival rates than men, possibly due to hormonal differences or differences in exposure to asbestos.
- Stage of cancer: As discussed above, the stage of the cancer at diagnosis is a significant predictor of survival.
- Type of mesothelioma: There are several types of mesothelioma, including pleural (lung) mesothelioma, peritoneal (abdominal) mesothelioma, and pericardial (heart) mesothelioma. Survival rates vary by type.
- Cell type: Mesothelioma can be classified into three cell types: epithelioid, sarcomatoid, and biphasic (a combination of the other two). Epithelioid mesothelioma tends to have the best prognosis, while sarcomatoid mesothelioma has the worst.
- Treatment: Patients who receive multimodal treatment, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, tend to have better survival rates than those who only receive one type of treatment.
- Overall health: Patients with good overall health, including a strong immune system, tend to have better survival rates than those who are already weakened by other medical conditions.
 Lifeyet News Lifeyet News
Lifeyet News Lifeyet News